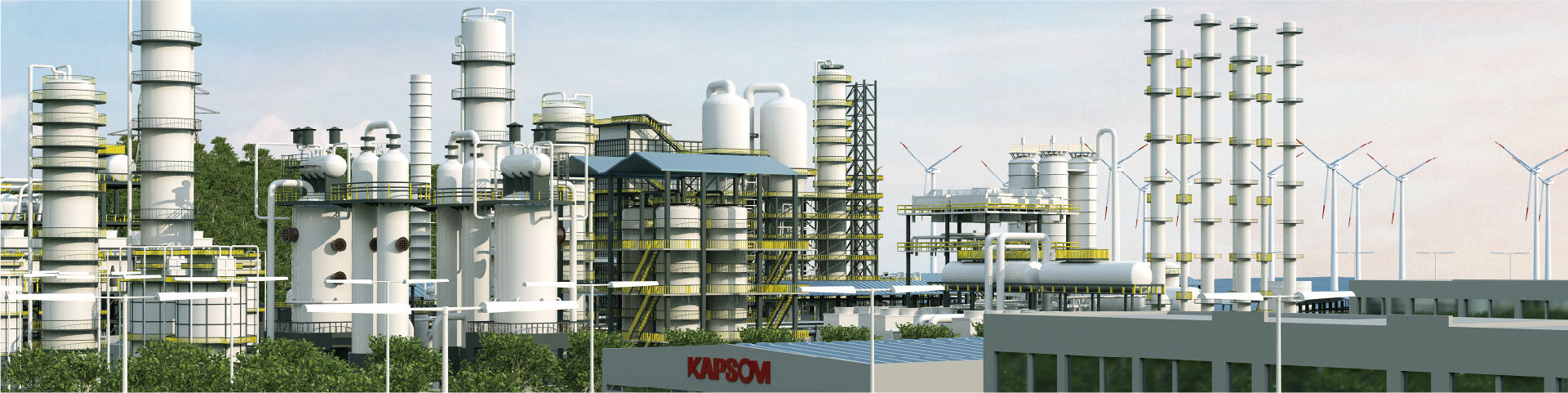
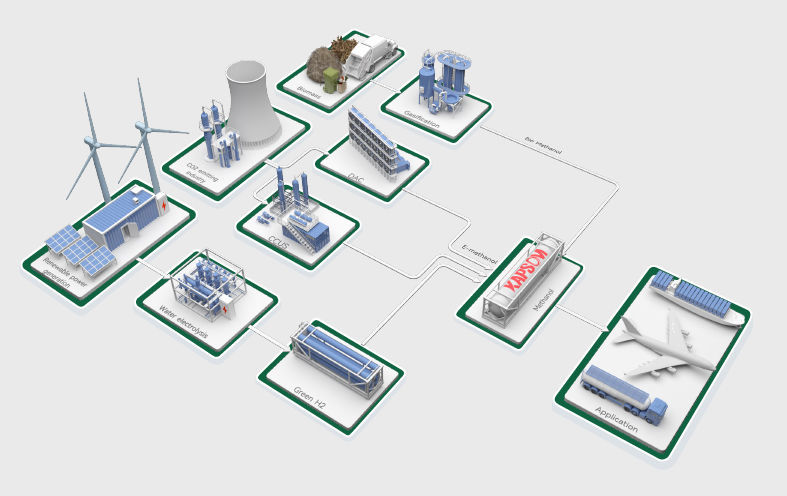
Methanol, as an essential industrial raw material and energy carrier, finds significant applications in both the traditional chemical and energy sectors. Green methanol, often referred to as methanol produced with extremely low or zero carbon emissions during its manufacturing process, stands in contrast to traditional coal-to-methanol production methods. In this innovative approach, carbon dioxide and hydrogen gas can be synthesized into methanol under catalytic conditions, effectively promoting the utilization of carbon dioxide resources.
Green methanol holds immense potential in decarbonizing the transportation sector. It can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by up to 95%, decrease nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by as much as 80%, and completely eliminate sulfur oxides (SOx) and particulate matter emissions. Green methanol (CH3OH) presents a promising avenue for decarbonization in the chemical industry, automotive applications, and energy-intensive industries. It offers a fresh perspective for the fuel market and represents a new pathway to establishing sustainable industries.

The effects of increased greenhouse gas emissions threaten coastal and marine ecosystems through changes in ocean temperatures and melting ice, which in turn affects ocean currents, weather patterns and sea levels.





Green methanol finds extensive applications in the industrial sector, such as serving as a raw material for plastic production and as a potential sustainable fuel in the maritime industry. According to the Methanol Institute, green methanol can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 60-95% compared to traditional fuels like gasoline or diesel. It also has lower sulfur content, reducing emissions of sulfur oxides that contribute to air pollution and acid rain.
It is a versatile fuel that can be used in internal combustion engines, hybrid vehicles, fuel cell vehicles, and ships. It remains in liquid form at ambient temperatures and pressures, making it easy to store, transport, and distribute. It is compatible with existing distribution infrastructure and can be blended and stored alongside traditional fuels.
Furthermore, green methanol-related projects are being implemented in various locations worldwide, indicating the potential for rapid expansion in the global green methanol market.

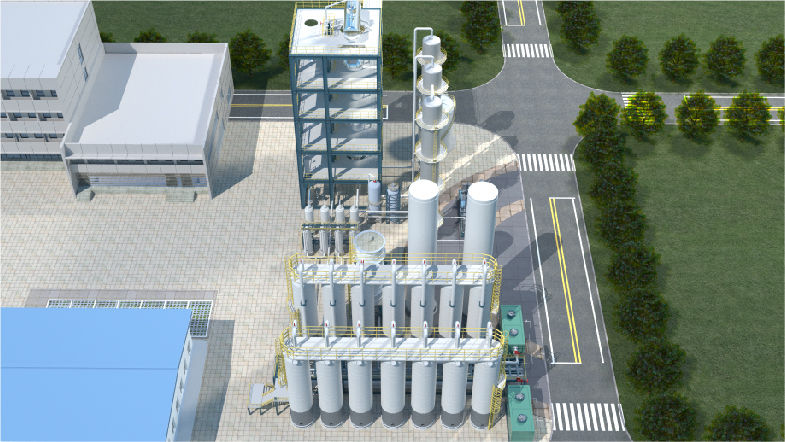
The uniqueness of KAPSOM in biomass methanol production lies in its intelligent management system, which ensures the accuracy and adaptability of the entire process. The equipment is designed to operate at low to medium pressures and offers a wide temperature range of 200~300C, allowing it to flexibly adapt to diverse process conditions.
At the same time, the integration of single-series designs significantly improves the overall efficiency of the production system. This simplified approach not only ensures a more compact operating space but also maximizes resource utilization. The equipment’s production scale ranges from 10 to 1200kt/a, making it one of the first choices for sustainable and large-scale methanol production. KAPSOM biomass methanol production stands out with its intelligent control system, flexible operating parameters and efficient single-series design, setting a new benchmark for sustainable production.

KAPSOM is committed to the design of high-efficiency biomass methanol reactors, with unique features of water bed run-off reactors and natural circulation of water vapor, emphasizing the optimal efficiency and sustainability of biomass methanol production. The core of the innovation is the water bed run-off reactor, which ensures uniform distribution of reaction materials and significantly improves the overall reaction efficiency. The advanced design not only promotes reaction process uniformity but also maximizes yield.
Additionally, the integration of natural circulation of water vapor adds another layer of efficiency to the system. This strategic approach not only improves energy efficiency and reduces overall operating costs, but also reduces reliance on external energy sources. This dual advantage not only drives economic sustainability but is also consistent with the broader goal of creating more environmentally friendly and resource-saving production processes.

KAPSOM uses state-of-the-art equipment to produce high-purity biomass methanol, minimizing the presence of by-products and impurities and increasing the overall purity of the final product. In addition, the reduction of by-products and impurities helps streamline subsequent processing procedures, resulting in simpler, more efficient manufacturing workflows. This not only demonstrates KAPSOM’s commitment to providing high-quality methanol, but also underlines our commitment to optimizing production efficiency and minimizing costs throughout the process.

| HYDROGEN GENERATION UNIT | 4.4~4.6 kWh/Nm3 (DC) Hydrogen |
| Single Set Maximum Capacity | |
| 1,000~1,500 Nm3/h (stable operation) | |
| DMW COSUMPTION~1kg Water/1Nm3 H2 | |
| Service Life: ≥160,000 hours |
| METHANOL SYNTHESIS UNIT | Low and Medium Pressure Reaction 3.0~5.0 MPa |
| 200~300℃ | |
| 10-1,200kt/a: Single Series Design | |
| Water Bed Radial Flow Reactor | |
| Natural Circulation of Water Vapor | |
| Reaction Temperature is Easy to Control, and the Adjustment is Convenient & Effective | |
| High Content of Crude Methanol with Few By-products & Impurities |
| METHANOL SYNTHESIS CATALYST | Black Cylinder With Spherical Caps of Two Ends (CuO, ZnO and Al2O3) |
| Service Life: 3~5 years | |
| Size:Φ5mmx(4~5)mm | |
| Specific Surface Area:>60m2/g | |
| Bulk Density:1.2 kg/L±0.05kg/L |
KAPSOM produces biomass methanol from renewable biomass, converts the biomass into syngas, and then forms methanol through a catalytic reaction. The carbon source of this methanol comes from atmospheric carbon dioxide absorbed by plants, achieving theoretical carbon neutrality and contributing to environmental sustainability. This innovative production method is based on plant-based raw materials and is more environmentally friendly and sustainable than traditional petrochemical methods. KAPSOM is committed to promoting clean energy and sustainable development, and has made substantial efforts to achieve a greener energy future through the production of biomass methanol.


When biomass is combusted or gasified to produce syngas (a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen), CO2 is released. This CO2 can be captured and utilized in the methanol synthesis process.

Waste-to-energy facilities that incinerate municipal solid waste release CO2. If the waste includes biomass components,this CO2 can be captured for methanol production.

Anaerobic digestion of organic waste produces biogas, which contains methane (CH4) and CO2. The CO2 from biogas can be separated and utilized for methanol synthesis.

Certain industrial processes release concentrated streams of CO2. Biomass methanol modules located near these processes can capture and use this CO2.

Biomass feedstocks from agricultural residues may include carbon that was captured from the atmosphere during plant growth. This carbon is released as CO2 during biomass processing.

Certain biomass feedstocks, such as sugars or organic wastes, can undergo fermentation processes to produce bioethanol or other biofuels, releasing CO2 as a byproduct. This CO2 can be captured for methanol synthesis.





In June 2022, KAPSOM entered into a partnership with a European company to initiate a sustainable methanol project aimed at producing 50,000 tons annually. The process involves utilizing renewable energy to electrolyze water, generating green hydrogen. Subsequently, this green hydrogen is combined with carbon dioxide to synthesize methanol. Upon the project’s completion, the initiative is expected not only to decrease carbon emissions but also to yield green, low-carbon fuels. This approach will significantly mitigate air pollution from industrial operations and fully embrace the high-value, comprehensive utilization of resources.

In 2023, KAPSOM forged a strategic alliance with Asia’s PGC New Energy Enterprises to embark on a groundbreaking project. The objective is to attain an annual production milestone of 20,000 tons of green methanol, leveraging advanced plasma technology and environmentally friendly methanol processes. Through the integration of biomass green methanol production, plasma carbon conversion technology for reduced carbon dioxide emissions, and green hydrogen production via water electrolysis, this initiative is poised to serve as a prominent commercial model in Carbon Capture and Utilization(CCU). Its success is anticipated to play a pivotal role in advancing global carbon neutrality efforts.
